New Book | Never Broken: Visualizing Lenape Histories
The exhibition was on view at the James A. Michener Art Museum in Doylestown, Pennsylvania this time last year (September 2023 – January 2024); the catalogue is still available from Penn Press:
Joe Baker and Laura Igoe, eds., Never Broken: Visualizing Lenape Histories (Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press, 2024), 96 pages, ISBN: 978-1879636163, $30.
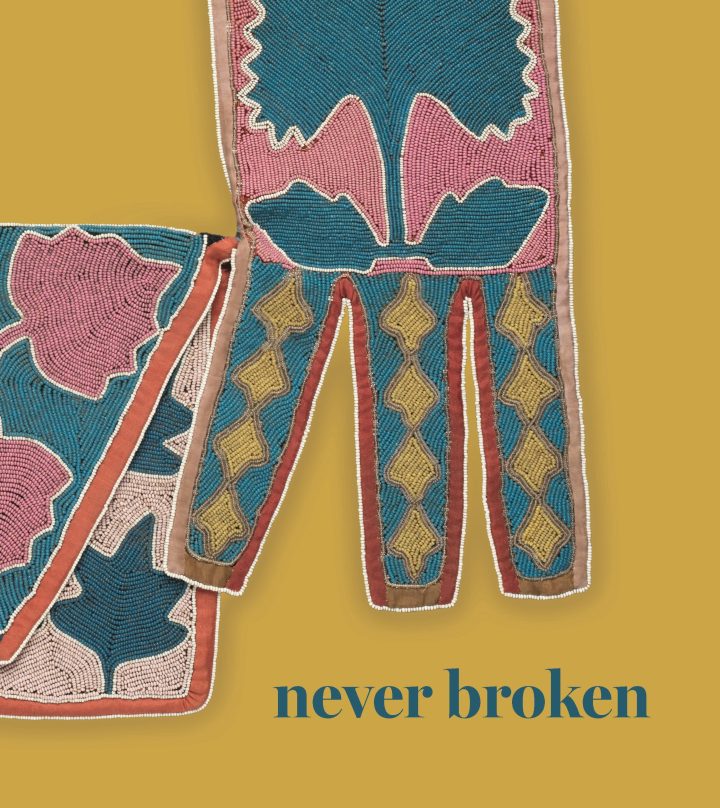 Through a focus on Lenape art, culture, and history and a critical examination of historical visualizations of Native and European American relationships, Never Broken explores the ways in which art can create, challenge, and rewrite history. This richly illustrated volume features contemporary work by Lenape artists in dialogue with historic Lenape ceramics, beadwork, and other cultural objects as well as re-creations of Benjamin West’s painting Penn’s Treaty with the Indians by European American artists. Published in conjunction with the first exhibition in Pennsylvania of contemporary Lenape artists who can trace their families back to the time of William Penn, Never Broken includes essays by Laura Turner Igoe, Joel Whitney, and Joe Baker. Igoe argues that the plethora of prints, paintings, and decorative arts that incorporated imagery from West’s iconic painting over a century after the depicted event attempted to replace the fraught history of Native and Anglo-American conflict with a myth of peaceful coexistence and succession. Whitney’s essay provides an overview of the culture of the Lenape and their forced removal out of Pennsylvania and the northeast to Oklahoma, Wisconsin, and Ontario. Finally, Baker highlights how he and the other contemporary Lenape artists featured in the exhibition, including Ahchipaptunhe (Delaware Tribe of Indians and Cherokee), Holly Wilson (Delaware Nation and Cherokee), and Nathan Young (Delaware Tribe of Indians, Pawnee, and Kiowa), tell their own stories rooted in memory, ancestry, oral history. Their work underscores the continuing legacy and evolution of Lenape visual expression and cross-cultural exchange, reasserts the agency of their Lenape ancestors, and establishes that the Lenape’s ties to the area were—unlike Penn’s Treaty—never broken.
Through a focus on Lenape art, culture, and history and a critical examination of historical visualizations of Native and European American relationships, Never Broken explores the ways in which art can create, challenge, and rewrite history. This richly illustrated volume features contemporary work by Lenape artists in dialogue with historic Lenape ceramics, beadwork, and other cultural objects as well as re-creations of Benjamin West’s painting Penn’s Treaty with the Indians by European American artists. Published in conjunction with the first exhibition in Pennsylvania of contemporary Lenape artists who can trace their families back to the time of William Penn, Never Broken includes essays by Laura Turner Igoe, Joel Whitney, and Joe Baker. Igoe argues that the plethora of prints, paintings, and decorative arts that incorporated imagery from West’s iconic painting over a century after the depicted event attempted to replace the fraught history of Native and Anglo-American conflict with a myth of peaceful coexistence and succession. Whitney’s essay provides an overview of the culture of the Lenape and their forced removal out of Pennsylvania and the northeast to Oklahoma, Wisconsin, and Ontario. Finally, Baker highlights how he and the other contemporary Lenape artists featured in the exhibition, including Ahchipaptunhe (Delaware Tribe of Indians and Cherokee), Holly Wilson (Delaware Nation and Cherokee), and Nathan Young (Delaware Tribe of Indians, Pawnee, and Kiowa), tell their own stories rooted in memory, ancestry, oral history. Their work underscores the continuing legacy and evolution of Lenape visual expression and cross-cultural exchange, reasserts the agency of their Lenape ancestors, and establishes that the Lenape’s ties to the area were—unlike Penn’s Treaty—never broken.
Joe Baker is an artist, educator, curator, and culture bearer who has been working in the field of Native Arts for the past thirty years. He is an enrolled member of the Delaware Tribe of Indians of Oklahoma and co-founder and executive director of the Lenape Center in Manhattan. His work is included in the permanent collection of the Metropolitan Museum of Art and numerous other museums and collections in the United States and Canada, including the American Museum of Art and Design.
Laura Turner Igoe is the Gerry and Marguerite Lenfest Chief Curator at the James A. Michener Art Museum in Doylestown, Pennsylvania. At the Michener, she curated Impressionism to Modernism: The Lenfest Collection of American Art (2019), Rising Tides: Contemporary Art and the Ecology of Water (2020), and she co-curated Through the Lens: Modern Photography in the Delaware Valley (2021) and Daring Design: The Impact of Three Women on Wharton Esherick’s Craft (2021–22).
c o n t e n t s
Foreword and Acknowledgements — Vail Garvin
Introduction — Joe Baker and Laura Turner Igoe
Penn’s Treaty with the Indians: Myth-Making across Media — Laura Turner Igoe
Violence and the Forced Removals of the Lenape — Joel Whitney
Nèk Elànkumàchi Maehëleyok: The Relatives Gathered — Joe Baker
Plates
Contributors
New Book | Native Nations: A Millennium in North America
From Penguin Random House:
Kathleen DuVal, Native Nations: A Millennium in North America (New York: Random House, 2024), 752 pages, ISBN: 978-0525511038, $38.
 Finalist for the Cundill History Prize
Finalist for the Cundill History Prize
Long before the colonization of North America, Indigenous Americans built diverse civilizations and adapted to a changing world in ways that reverberated globally. And, as award-winning historian Kathleen DuVal vividly recounts, when Europeans did arrive, no civilization came to a halt because of a few wandering explorers, even when the strangers came well armed.
A millennium ago, North American cities rivaled urban centers around the world in size. Then, following a period of climate change and instability, numerous smaller nations emerged, moving away from rather than toward urbanization. From this urban past, egalitarian government structures, diplomacy, and complex economies spread across North America. So, when Europeans showed up in the sixteenth century, they encountered societies they did not understand—those having developed differently from their own—and whose power they often underestimated.
For centuries afterward, Indigenous people maintained an upper hand and used Europeans in pursuit of their own interests. In Native Nations, we see how Mohawks closely controlled trade with the Dutch—and influenced global markets—and how Quapaws manipulated French colonists. Power dynamics shifted after the American Revolution, but Indigenous people continued to command much of the continent’s land and resources. Shawnee brothers Tecumseh and Tenskwatawa forged new alliances and encouraged a controversial new definition of Native identity to attempt to wall off U.S. ambitions. The Cherokees created institutions to assert their sovereignty on the global stage, and the Kiowas used their power in the west to regulate the passage of white settlers across their territory.
In this important addition to the growing tradition of North American history centered on Indigenous nations, Kathleen DuVal shows how the definitions of power and means of exerting it shifted over time, but the sovereignty and influence of Native peoples remained a constant—and will continue far into the future.
Kathleen DuVal is a professor of history at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, where she teaches early American and American Indian history. Her previous work includes Independence Lost, which was a finalist for the George Washington Prize, and The Native Ground: Indians and Colonists in the Heart of the Continent. She is a coauthor of Give Me Liberty! and coeditor of Interpreting a Continent: Voices from Colonial America.
Exhibition | Colonial Crossings: The Spanish Americas

Unidentified workshop, Cuzco, Peru, Our Lady of the Rosary of Chiquinquirá with Female Donor, late 17th–early 18th century, oil and gold on canvas (Collection of Carl & Marilynn Thoma, 2013.046; photo by Jamie Stukenberg).
◊ ◊ ◊ ◊ ◊
Now on view at Cornell’s Johnson Museum of Art:
Colonial Crossings: Art, Identity, and Belief in the Spanish Americas
Johnson Museum of Art, Cornell University, Ithaca, New York, 20 July 2024 — 15 December 2024
Curated by Andrew Weislogel and Ananda Cohen-Aponte, with students in the course Colonial Connectivities: Curating the Arts of the Spanish Americas
The artworks featured in this exhibition span more than three hundred years of history, five thousand miles of territory, and two oceans, introducing the rich artistic traditions of Mexico, Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Cuba, Puerto Rico, and the Philippines during the period of Spanish colonial rule (approximately 1492–1830).
This first exhibition of colonial Latin American art at Cornell considers the profound impact of colonization, evangelization, and the transatlantic slave trade in the visual culture of the Spanish empire, while also manifesting the creative agency and resilience of Indigenous, Black, and mixed-race artists during a tumultuous historical period bookended by conquest and revolution.
At first glance, these religious images, portraits, and luxury goods might seem to uphold colonial structures that suggest a one-way flow of power from Europe to the Americas. Yet closer consideration of these artists’ identities, materials, techniques, and subjects reveals compelling stories about the global crossings of people, commodities, and ideas in the creation of new visual languages in the Spanish Americas. These artworks testify to entangled cultural landscapes—from paintings of the Virgin Mary with ties to sacred sites of her apparition, to lacquer furniture bearing the visual stamp of trade with East Asia, they embody a plurality of cultural, material, and religious meanings.

Unidentified workshop, Peru, Our Lady of Cocharcas, 1751, oiil and gold on canvas (Collection of Carl & Marilynn Thoma, 2011.040; photo by Jamie Stukenberg).
Colonial Crossings was curated by Dr. Andrew C. Weislogel, Seymour R. Askin, Jr. ’47 Curator of Earlier European and American Art at the Museum, and Dr. Ananda Cohen-Aponte, Associate Professor of the History of Art & Visual Studies, and the students in Colonial Connectivities: Curating the Arts of the Spanish Americas (ARTH 4166/6166):
Osiel Aldaba ’26
Miguel Barrera ’24
Daniel Dixon ’24
Juliana Fagua Arias, PhD student
Miche Flores, PhD student
Isa Goico ’24
Sara Handerhan ’24
Emily Hernandez ’25
Ashley Koca ’25
Maximilian Leston ’26
Maria Mendoza Blanco ’26
Lena Sow, PhD student
Nicholas Vega ’26
We are grateful to lenders Carl and Marilynn Thoma, the Denver Museum of Art, the Hispanic Society of America, and the Division of Rare and Manuscript Collections, Cornell University Library; and to David Ni ’24, the 2023 Nancy Horton Bartels ’48 Scholar for Collections, for organizational support.

Unidentified artist, Quito, Ecuador, Noah’s Ark, detail, late 18th century, oil on canvas (Collection of Carl & Marilynn Thoma, 2000.004).
◊ ◊ ◊ ◊ ◊
The Johnson Museum will also present this symposium:
Symposium | Reimagining the Américas: New Perspectives on Spanish Colonial Art
Online and in-person, Saturday, 9 November 2024
At this free symposium, presented in conjunction with the exhibition, established scholars whose work encompasses a variety of regions and approaches to colonial Latin American art history will offer new methodologies, seeking to expand the boundaries of this visual culture. Presentations will explore the exhibition’s thematic emphases on materiality and sacredness, hybridity and cross-cultural exchange, colonial constructions of race, and recovering art histories marked by silence and erasure.
• Time-Warping the Museum: Temporal Juxtapositions in Displays of Spanish Colonial Art — Lucia Abramovich, Museum of Fine Arts, Boston
• Framing Miracles for a New World: The Oval — Jennifer Baez, University of Washington
• Trent as Compass: Directions, Circuits, and Crossings of the Visual and Canonical in Spanish America — Cristina Cruz González, Oklahoma State University
• Splendor and Iridescence: Pearls in the Art of the Spanish Americas — Mónica Dominguez Torres, University of Delaware
• ‘Your Plenteous Grandeur Resides in You’: Asian Luxury in Spanish American Domestic Interiors — Juliana Fagua Arias, Cornell University
• Supplicant Africans: From Baptizands to Emblems of Abolition —Elena FitzPatrick Sifford, Muhlenberg College
• Voices of Influence: Exploring Power Dynamics in the Conservation of Musical Heritage in Colonial Latin America — Patricia García Gil, Cornell University
• Invisible Soldiers and Constant Servants: The Pre-Hispanic Roots of the Andean Cult of Angels — Maya Stanfield-Mazzi, University of Florida
A schedule will be posted soon. Please email eas8@cornell.edu to register in advance for in-person attendance. Click here to join the webinar.
Call for Papers | Global Material Culture and the Body, BSECS 2025 Panel
From HECAA:
Panel | Global Material Culture and the Body
British Society for Eighteenth-Century Studies Conference, Pembroke College, Oxford, 8–10 January 2025
Panel organized by Chloe Wigston Smith
Proposals for this session due by 18 October 2024
 Jointly supported by the Historians of Eighteenth-Century Art and Architecture and the University of York’s Center for Eighteenth Century Studies, this panel aims to foster interdisciplinary conversations about the relations between global material culture and the body, in keeping with the theme of the 54th annual BSECS conference, Bodies and Embodiment. Papers might focus on the body’s physical proximity to examples of global material culture, whether in the form of clothes, accessories, cosmetics, and domestic furnishings (and more); the body’s haptic experience of global objects, through making, production, handling, and consumption; and / or the representation of the body and bodies on specific objects. Papers might focus on a wide range of print, visual, and material sources, including ceramics, drawings, watercolours, handiwork, woodwork, etc, and / or the broad range of materials in the period, such as cotton, indigo, or silver. Submissions from early career scholars are especially encouraged. Please submit abstracts of no more than 350 words along with a short (1 page) CV to Chloe Wigston Smith at chloe.wigstonsmith@york.ac.uk.
Jointly supported by the Historians of Eighteenth-Century Art and Architecture and the University of York’s Center for Eighteenth Century Studies, this panel aims to foster interdisciplinary conversations about the relations between global material culture and the body, in keeping with the theme of the 54th annual BSECS conference, Bodies and Embodiment. Papers might focus on the body’s physical proximity to examples of global material culture, whether in the form of clothes, accessories, cosmetics, and domestic furnishings (and more); the body’s haptic experience of global objects, through making, production, handling, and consumption; and / or the representation of the body and bodies on specific objects. Papers might focus on a wide range of print, visual, and material sources, including ceramics, drawings, watercolours, handiwork, woodwork, etc, and / or the broad range of materials in the period, such as cotton, indigo, or silver. Submissions from early career scholars are especially encouraged. Please submit abstracts of no more than 350 words along with a short (1 page) CV to Chloe Wigston Smith at chloe.wigstonsmith@york.ac.uk.
Please note that selected presenters will need to become members of BSECS to register for the conference. Or BSECS honors ASECS memberships, so if you are an ASECS member you will not need to join BSECS.



















leave a comment